- About Us
- Bearings
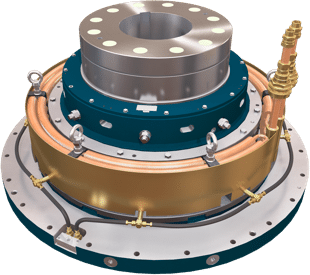 Vertical Bearings
Vertical Bearings
- AV Series
AV
LV SeriesLV
MV SeriesMV
V SeriesV
 Horizontal Bearings
Horizontal Bearings
- HD Series
HD
IH SeriesIH
 Tilting Pad Bearings
Tilting Pad Bearings
 Journal Bearings
Journal Bearings
- Journal Pad Units
Journal
 Thrust Bearings
Thrust Bearings
- SE Series
SE
Omega EqualisedOmega
OmegaOmega
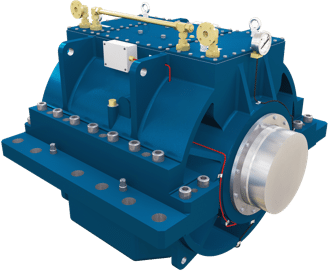 Marine Bearings
Marine Bearings
- Marine Gearbox Internals
Marine
Marine Propulsion Motor
and Generator BearingsEnter your email to download the full paper
"*" indicates required fields
Outline
Home > Two Case Studies for the use of PTFE Thrust Bearings in Hydropower ApplicationsTwo Case Studies for the use of PTFE Thrust Bearings in Hydropower Applications
R T Knox, Michell Bearings, UK, J E L Simmons, Heriot-Watt University, UK
Introduction
In any hydropower scheme the main load carrying bearings at the interface between stationary and moving parts of the system are of crucial importance to the long-term availability of generating capacity and robustness of supply. The tilting pad, fluid film bearings typically used in hydropower applications are based on wellproven engineering and, in most cases, extremely reliable. Nevertheless, bearing-related problems that thrnaten operations can arise for a variety of reasons. Typical causes are changes in the operating regime of the plant compared with the original specification or engineering interventions, for example in the fotm of design changes, in other parts of the assembly that impact adversely on the overall system.
This paper provides case study descriptions of two such major problems occurring in the main bearings of hydropower equipment. In both cases the problems were resolved by the installation of replacement bearings in which one of the working surfaces is covered with a layer of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroetlrylene). PTFE-faced fluid film bearings have been used for many years in the former Soviet Union, China and Eastern Europe. Advantages claimed for these bearings, in comparison with their conventional, whitemetal (babbitt)-faced counterparts, are increased load carrying capacity in normal use and removal of the need for high pressure oil injection. In conventional whitemetal bearings high pressure oil injection is used to reduce friction at start up, when stopping the bearing and in the course of maintenance procedures that require the main shaft to be rotated.
ACCESS FULL PAPERRecommended articles
PTFE Faced Bearings; Thissavros – A Case Study
PTFE Faced Thrust Bearings – An OEM’s Viewpoint
PTFE Faced Bearings for Marine Propulsion Applications
PTFE Bearing Technology for Thrust and Journal Applications
Michell Bearings
Waldridge Way,
Simonside East Industrial Park,
South Shields,
NE34 9PZ.Tel: +44 (0) 191 273 0291
Email: sales@michellbearings.com
Email: hrteam@britishengines.com
Email: recruitment@britishengines.com© Michell Bearings.
Registered Office Address: 11 Glasshouse Street, St Peter's, Newcastle upon Tyne. NE6 1BS. Company registered in England and Wales no. 9390648

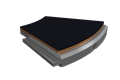 PTFE Bearings
PTFE Bearings